
How To Stop Ransomware Attacks
What is ransomware, why is it such an effective method of attack, and how can you stop ransomware attacks?

Ransomware is an advanced form of cyberattack, and one of the most harmful threats that security teams around the world are facing. Ransomware is used to target all organizations, from small teams to large enterprises, state systems and government networks.
While simple in concept, ransomware is uniquely damaging. It’s is a form malware that, when downloaded to a device, scrambles or deletes all data until a ransom is paid to restore it. Research suggests that in 2020 a new organization will be hit by a ransomware attack every 14 seconds. It has the potential to cripple networks and cause catastrophic harm to infrastructure.
One of the most famous examples of ransomware is the WannaCry ransomware attack. WannaCry was a piece of malware that infected over 230,000 computers across 150 companies within a single day. It encrypted all files it found on a device and requested users pay $300 worth of bitcoin payments to restore them.
WannaCry for the most part affected large organizations; the National Health Service in the UK being one of highest profile targets affected. Amazingly, the attack’s impact was lower than it could have been, due to the fact it was stopped relatively quickly, and it didn’t target highly critical infrastructure, like railways or nuclear power plants.
Even so, economic losses from the attack the millions of dollars. More recently, 22 cities in Texas have been hit by ransomware attacks, with attackers demanding $2.5 million to restore encrypted files, leading to a federal investigation. There were a staggering 500 million ransomware attacks reported in 2021.
So, how can you stop ransomware attacks?
How Does Ransomware Work?
Ransomware begins with malicious software being downloaded onto an endpoint device, like a desktop computer, laptop or smartphone. This usually happens because of user error and ignorance of security risks.
One common method of distributing malware is through phishing attacks. This involves an attacker attaching an infected document or URL to an email, while disguising it as being legitimate to trick users into opening it, which will install the malware on their device.
Another popular method of spreading ransomware is using a ‘trojan horse’ virus style. This involves disguising ransomware as legitimate software online, and then infecting devices after users install this software.
Encrypting Files
Ransomware typically works very quickly. In seconds, the malicious software will take over critical process on the device, and search for files to be encrypted, meaning all of the data within them is scrambled. The ransomware will likely delete any files it cannot encrypt.
The ransomware will then infect any other hard-drives or USB devices connected to the infected host machine. Any new devices or files added to the infected device will also be encrypted after this point. Then, the virus will begin sending out signals to all of the other devices on the network, to attempt to infect them as well.
This whole process happens extremely quickly, and in just a few minutes the device will display a message that looks like this:
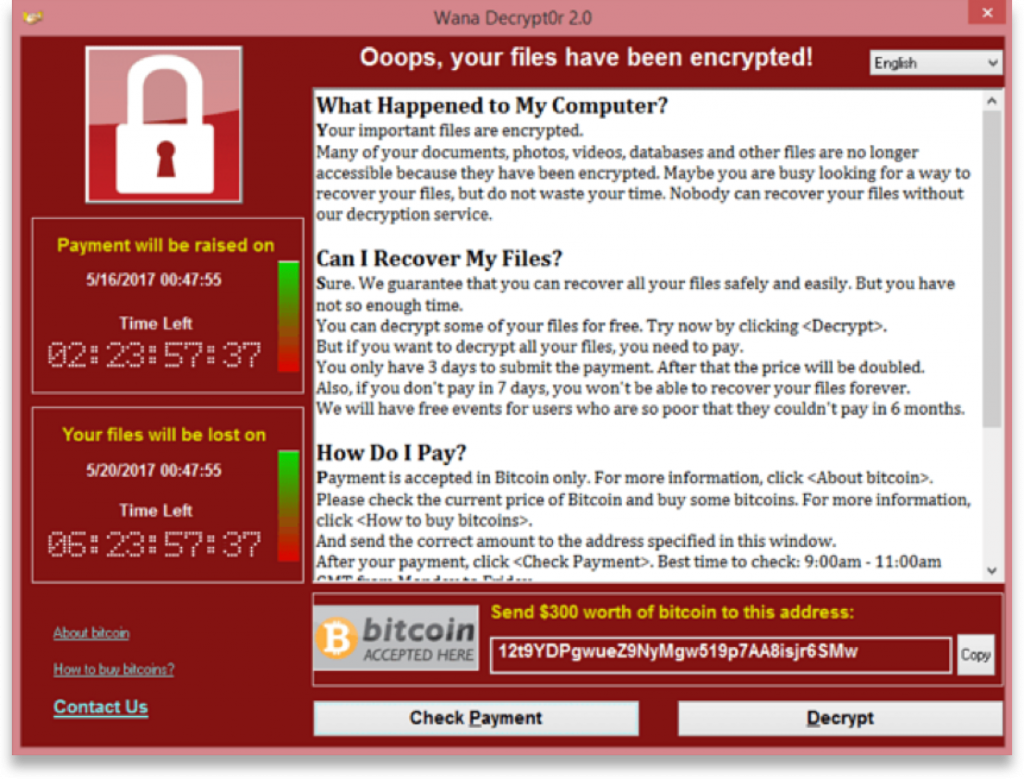
This is the message that displayed to users who were infected with the WannaCry ransomware attack. As you can see, it’s a ‘cyber blackmail’ note, which tells users that their files are locked, and that if a payment is not made, they will be deleted.
Payments will likely be requested in bitcoin, as this payment method cannot be traced, and there is often a countdown, which puts pressure on companies to act quickly in making payments to attackers.
There are different types of ransomware. Some threaten to release the encrypted data to the public, which may be damaging to companies who need to protect customer or business data. There is also scareware, that floods the computer with pop-up and demand a ransom to solve the issue. The same principle is always involved – a malicious program infects the computer and a payment is requested to remove it.
Why is Ransomware so Effective?
Ransomware can be hugely damaging to businesses, causing loss of productivity and often financial losses. Most obviously there is the loss of files and data, which may represent hundreds of hours of work, or customer data that is critical to the smooth running of your organization.
There is also the loss of productivity as machines will be unusable. Then of course there is the financial loss of needing to replace infected machines, pay for an IT company to remediate against the attack and put protection in place to stop it happening again.
For these reasons many businesses feel they have no choice but to pay the ransom, although it is highly recommended that they do not. Ransomware generates over $25 million in revenue for hackers each year, which demonstrates how effective it is to extort money from organizations.
Ransomware Targets Human Weaknesses
By targeting people with phishing attacks, attackers can bypass traditional security technologies with ransomware. Email is a weak point in many businesses’ security infrastructure, and hackers can exploit this by using phishing emails to trick users into opening malicious files and attachments. By using trojan horse viruses, hackers also target human error by causing them to inadvertently to download malicious files.
The major issue here is a lack of awareness about security threats from most users, with many people unaware of what threats look like, and what they should avoid downloading or opening on the internet or in emails. This lack of security awareness helps ransomware to spread much more quickly.
Lack of strong Technological Defences
Ransomware attacks are growing by a record amount, with attackers developing increasingly sophisticated malware. Many businesses do not have the strong defences needed in place to block these attacks, because they can be expensive and complicated to deploy and use. It’s often hard for IT teams to convince company executives that they need strong security defences until it’s too late and systems have already been compromised.
Out of Date Hardware and Software
Alongside not having strong defences against attacks, many organizations also rely too heavily on hardware and software that is out of date. Over time, attackers discover security vulnerabilities. Technology companies often push out security updates, but for many organizations they have no way to verify that users are installing this updates. Many organizations also rely heavily on older computers that are no longer supported, meaning they are open to vulnerabilities.
This is one of the main reasons the WannaCry virus was so successful. It targeted many large organizations like the NHS, which for most part uses decades old machines on operating systems that are no longer regularly supported with updates. The exploit WannaCry used to infect systems was actually discovered two months before the attack took place and was patched by Microsoft. However, devices were not updated, and so the attack still rapidly spread.
How Can You Stop Ransomware?
The best way for businesses to stop ransomware attacks is to be proactive in your security approach and ensure that you have strong protections in place before ransomware can infect your systems. Here are some tips for the best protections to put in place to stop ransomware attacks:
Strong, Reputable Endpoint Anti-Virus Security
One of the most important ways to stop ransomware is to have a very strong endpoint security solution. These solutions are installed on your endpoint devices, and block any malware from infecting your systems. They also give admins the ability to see when devices have been compromised, and ensure that security updates have been installed.
Read: Our Guide To The Top Endpoint Security Solutions
This solutions can help protect against malicious downloads, and can alert users when they are visiting risky websites. These systems are not guaranteed to be 100% effective as cybercriminals are always trying to create new pieces of malware that can get around the security tools, but endpoint security is a crucial step in strong protection against malware.
Email Security, Inside and Outside the Gateway
As ransomware is commonly delivered through email, email security is crucial to stop ransomware. Secure Email gateway technologies filter email communications with URL defences and attachment sandboxing to identify threats and block them from being delivered to users. This can stop ransomware from arriving on endpoint devices and block users from inadvertently installing ransomware onto their device.
Read Next: Our Guide To The Top 11 Secure Email Gateways
Ransomware is also commonly delivered through phishing. Secure email gateways can block phishing attacks, but there is also Post-Delivery Protection technologies, which use machine learning and AI algorithms to detect phishing attacks, and display warning banners within emails to alert them that an email may be suspicious. This helps users to avoid phishing emails which may contain a ransomware attack.
Web Filtering & Isolation Technologies
DNS Web filtering solutions stop users from visiting dangerous websites and downloading malicious files. This helps to block viruses that spread ransomware from being downloaded from the internet, including trojan horse viruses that disguise malware as legitimate business software.
Read Next: Our Guide To The Top DNS Filtering Solutions
DNS filters can also block malicious third party adverts. Web filters should be configured to aggressively block threats, and to stop users from visiting dangerous or unknown domains. Utilizing Isolation can also be an important tool to stop ransomware downloads. Isolation technologies completely remove threats away from users by isolating browsing activity in secure servers and displaying a safe render to users. This can help to prevent ransomware as any malicious software is executed in the secure container and does not affect the users themselves. The main benefit of Isolation is that it doesn’t impact the user’s experience whatsoever, delivering high security efficacy with a seamless browsing experience.
Read Next: Browser Isolation Guide for Business
Security Awareness Training
The people within your organization are often your biggest security risk. In recent years there has been a huge growth in Security Awareness Training platforms, which train users about the risks they face using the internet at work and at home. Awareness Training helps to teach users what threats within email look like, and best security practices they should follow to stop ransomware, such as making sure their endpoints are updated with the latest security software.
Read Next: Our Guide To The Top Security Awareness Training Solutions
Security Awareness Training solutions typically also provide phishing simulation technologies. This means admins can create customized simulated phishing emails, and send them out to employees to test how effectively they can detect attacks. Phishing simulation is an ideal way to help view your security efficacy across the organization, and is a useful tool to help identify users that need more security training to help stop the spread of ransomware.
Data Backup and Recovery
If a ransomware attack succeeds and your data is compromised, the best way to protect your organization is to be able to restore the data you need quickly and minimize the downtime. The best way to protect data is to ensure that it is backed up in multiple places, including in your main storage area, on local disks, and in a cloud continuity service. In the event of a ransomware attack, backing up data means you will be able to mitigate the loss of any encrypted files and regain functionality of systems.
Read Next: Our Guide To The Top Backup and Recovery Solutions for Office 365
The best Cloud Data Backup and Recovery platforms will allow businesses to recover data in the case of a disaster, will be available anytime, and will be easily integrated with existing cloud applications and endpoint devices, with a secure and stable global cloud infrastructure. Cloud data backup and recovery is an important tool to remediating against ransomware.
Don’t Let Ransomware Damage Your Organization
By following the above steps, you can begin to protect your organization against damaging ransomware attacks. Start by reading our guides to the top email security solutions, and top endpoint protection solutions below.



